Thyroid Diseases & Surgery
Thyroid Diseases & Surgery
The thyroid is part of the endocrine glands that make hormones to regulate physiological functions in your body, like metabolism (body temperature, sweating, energy consumed), keep the muscles, brain, heart and other organs working properly. Other endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, pineal gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands.
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the lower neck, under the larynx (voice box) and the two side lobes wrap around the front half of the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, right above the collarbone, having two halves (lobes) joined by a small tissue bar (isthmus.). You can’t always feel it when the thyroid is its normal size.
What is a thyroid disorder?
Diseases of the thyroid gland are very common that affect millions of people across the world. The most common thyroid problems are:
- A hyperactive gland (overproduction of thyroid hormones), called hyperthyroidism (e.g., Graves’ disease, toxic adenoma or toxic nodular goitre)
- An underactive gland (underproduction of thyroid hormones), called hypothyroidism (e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis)
- Thyroid enlargement can be caused by overactivity (as in Graves’ disease) or from under-activity (as in hypothyroidism). An abnormally enlarged thyroid gland is often called a “goitre.”
- Inflammation of the thyroid is called Thyroiditis. This is usually caused by a viral infection or autoimmune condition.
- Thyroiditis in some patients can be painful or have no symptoms at all.
- Thyroid cancer is an uncommon form of cancer, which is usually curable. Radiation, surgery, and hormone treatments may be used to treat thyroid cancer.
- Thyroid nodule is a small abnormal mass of thyroid cells or lump in the thyroid gland. Thyroid nodules are extremely common and fortunately very few are cancerous. They may overproduce thyroid hormones, causing hyperthyroidism, or do not produce any symptoms.
- Thyroid storm is a very rare form of hyperthyroidism in which extremely high production of two types of thyroid hormones i.e., triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), causing severe illness
Patients with a family history of thyroid cancer or who have received radiation therapy to the head or neck, possibly as a remedy for acne, adenoids, or other reasons are more prone to develop thyroid malignancy.
If you develop significant swelling in your neck or difficulty in swallowing or breathing, you should contact an ENT specialist immediately.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTS
Thyroid symptoms are easily confused with those of other conditions; therefore, it sometimes can be difficult to diagnose the thyroid disease. You may experience the same symptoms when you are ageing or pregnant and you would when developing thyroid disease. Fortunately, various tests can help determine if your symptoms are being caused by a thyroid issue. These tests include:
- Thyroid blood tests to check if your thyroid gland is functioning normally by measuring the level of thyroid hormones in your blood.
- Evaluation of the vocal cords/larynx with a mirror or a fiberoptic telescope
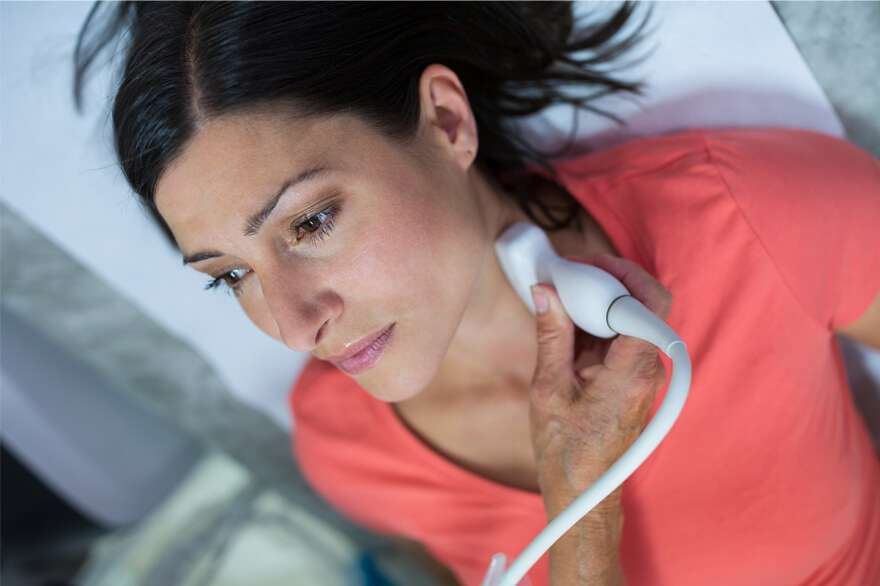
- An ultrasound examination of your thyroid and neck
- A radioactive thyroid scan
- A fine-needle aspiration biopsy
- A chest X-ray
- Image tests such as CT or CAT scan or MRI scan
- A Physical examination where your doctor feels your neck for any enlargement or growths of the thyroid
Thyroid disease treatment and surgery:
Your doctor’s goal is to return your thyroid hormone levels to normal and It can be done in different ways and each specific treatment will depend on the cause of your thyroid condition.
If you have hyperthyroidism (high levels of thyroid hormones), treatment options can include:
- Anti-thyroid drugs (propylthiouracil and methimazole): These are medications that stop your thyroid from making hormones.
- Radioactive iodine (RAI): This treatment given as a pill damages the cells of your thyroid, preventing it from making high levels of thyroid hormones.
- Beta-blockers: These medications don’t change the level of thyroid hormone being produced in your body, but they help prevent or control your symptoms.
- Surgery (Thyroidectomy): A more permanent form of treatment in which your doctor may surgically remove all or part of your thyroid This will stop it from producing hormones. However, thyroid replacement hormones need to be taken for the rest of your life
If you have hypothyroidism (low levels of thyroid hormones), the main treatment option is:
- Thyroid replacement medication: This drug is a synthetic (man-made version) way to add thyroid hormones back into your body. A drug that’s commonly used is called levothyroxine. Using medication is not a cure, but it can keep your thyroid condition under control and help you to live a normal life.
Meet Our Doctors

Dr. Aravind Kumar Alwala
MBBS (Osm)., MSENT specialist, Chief Endoscopic Sinus Surgeon
Make an Appointment
Dr. Laxmi Priya Pallapolu
MBBS (Gold Medalist)., MS Ophthal (FICO)Consultant Ophthalmologist, Chief Phaco Surgeon
Make an Appointment